April is Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) Awareness Month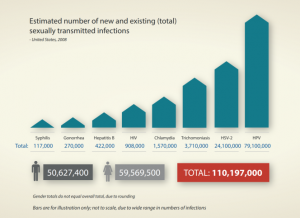 in the U.S., which aims to raise public awareness about the impact of STDs and the importance of preventing, testing for, and treating STDs. In addition, April 22-28 is National Infertility Awareness Week – a good time to talk about women’s health and the risks of infertility STDs can pose.
in the U.S., which aims to raise public awareness about the impact of STDs and the importance of preventing, testing for, and treating STDs. In addition, April 22-28 is National Infertility Awareness Week – a good time to talk about women’s health and the risks of infertility STDs can pose.
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are commonly spread from person to person via sexual contact. Also referred to as STIs (sexually transmitted infections) or venereal disease, they represent a significant women’s health issue - worldwide.
The WHO (World Health Organization) estimates there are more than 1 million new STIs acquired daily worldwide, with 1 in 4 sexually active adolescent females infected.
STIs are a Critical Women’s Health Issue
Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis and trichomoniasis – worldwide it is estimated that there are 357 million new infections out of these four STIs annually. In the United States alone, it is estimated nearly 20 million people acquire an STI each year, at a direct cost to the healthcare system of $16 billion dollars. STI’s do not discriminate – with men and women of all ages, backgrounds and economic levels impacted. However, according to a CDC Factsheet on ways in which STIs impact women differently from men, women disproportionately bear the long-term consequences of STIs.
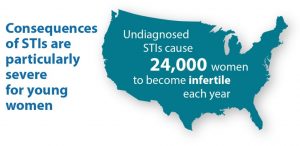
 Each year in the U.S. more than 9 million women are diagnosed with an STI. This is significant as women often have more serious STI-related health problems than men, which can have consequences beyond the immediate impact such as infertility and mother-to-child transmission. “For example, each year untreated STDs cause infertility in at least 24,000 women in the U.S., and untreated syphilis in pregnant women results in infant death in up to 40 percent of cases.” While globally, “Over 900,000 pregnant women were infected with syphilis resulting in approximately 350,000 adverse birth outcomes including stillbirth in 2012.”
Each year in the U.S. more than 9 million women are diagnosed with an STI. This is significant as women often have more serious STI-related health problems than men, which can have consequences beyond the immediate impact such as infertility and mother-to-child transmission. “For example, each year untreated STDs cause infertility in at least 24,000 women in the U.S., and untreated syphilis in pregnant women results in infant death in up to 40 percent of cases.” While globally, “Over 900,000 pregnant women were infected with syphilis resulting in approximately 350,000 adverse birth outcomes including stillbirth in 2012.”
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that – at any given time - 290 million women worldwide have a human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. Infection with HPV is very common and often resolves on its own, however when it does not go away it can lead to cervical and other cancers.
According to the CDC, some STIs, “are easily treated and cured if diagnosed early: chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and Trichomoniasis. However, too many of these infections go undetected because they often have no symptoms.” This is why appropriate testing for STIs is so important, to help detect and treat before complications arise and to help limit further spread of the infection.
- Trichomoniasis: The Most Common Curable STD
Trichomoniasis (or Trich)is considered the most common, curable STI.- It is a non-viral STI caused by a motile protozoan parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis.
- Trichomoniasis occurs at higher rates than other curable STIs such as Gonorrhea, Syphilis, and Chlamydia combined, and is more common in women than in men.
There are a number of complications associated with Trich, each of which carries health, social and economic costs:
- preterm labor & birth
- infertility
- increased risk of HIV/HSV
- cervical cancer
- pelvic inflammatory disease.
Trich is underdiagnosed and under-treated. It is estimated that around 80% of women and men with trich infections are asymptomatic. When testing for trichomonas, the various diagnostic choices are often limited by accuracy, timeliness, intended use, or cost (check out our earlier post on Trichomonas Rapid Point-of-Care Testing).
- Bacterial Vaginosis: Not an STI, But Increases Risk of STIs
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is an infection caused by changes in the balance between “good” bacteria and “bad” bacteria in the vagina. While not considered an STI, BV can lead to higher susceptibility to sexually-transmitted infections. Left untreated, BV can lead to an assortment of complications including endometriosis and an increased risk of pre-term delivery in pregnant women.
 The CDC states that it “is the most common vaginal infection in women ages 15 - 44.” It has been reported that “[w]orldwide, it is estimated that 20 – 30 % of women of reproductive age attending sexually transmitted infection (STI) clinics suffer from BV, the prevalence of which can be as high as 50 – 60 % in high-risk populations.” It has also been reported that the risk of BV for preterm delivery in the United States is 30% - at a cost of $1 billion per year.
The CDC states that it “is the most common vaginal infection in women ages 15 - 44.” It has been reported that “[w]orldwide, it is estimated that 20 – 30 % of women of reproductive age attending sexually transmitted infection (STI) clinics suffer from BV, the prevalence of which can be as high as 50 – 60 % in high-risk populations.” It has also been reported that the risk of BV for preterm delivery in the United States is 30% - at a cost of $1 billion per year.
A key objective in the fight against BV (and many other conditions) is the need for rapid, accurate diagnostic results – ideally in a single patient visit – in order to begin therapeutic treatment immediately.
Syphilis: Almost Eradicated, But Now on the Rise
Syphilis, a chronic infection caused by Treponema pallidum, was close to eradication and is now reaching 20 year highs in the U.S. The ECDC’s Annual Epidemiological report shows a steady rise across much of Europe, as well. Complications from syphilis can lead to:
- sores
- skin rash, swollen lymph nodes
- heart disease
- nerve disorders
- brain damage
- blindness
- aortic aneurism
Syphilis screening requirements vary from country to country, but all diagnoses require both screening and confirmatory testing (Read more in a previous post).
The Most Common STI Symptom? Not Having Any
Our immune systems fight hard to protect us from the symptoms of STIs, so it’s common for patients to be unaware of an infection. From trichomonas to bacterial vaginosis to syphilis, routine testing and safe sex practices are critical to ensuring women’s health.
Diagnostics for Sexually Transmitted Infections & Women’s Health
Sekisui Diagnostics provides a comprehensive set of diagnostic tools for a number of women’s health infections and sexually transmitted infections.
 Learn more about our rapid, CLIA-Waived, Point-of-Care Tests or view our educational Trichomonas video
Learn more about our rapid, CLIA-Waived, Point-of-Care Tests or view our educational Trichomonas video
For automated laboratory syphilis testing, learn more about our CE marked SEKURE® TPLA and RPR tests (not currently available in the U.S. or Canada)



Share Article